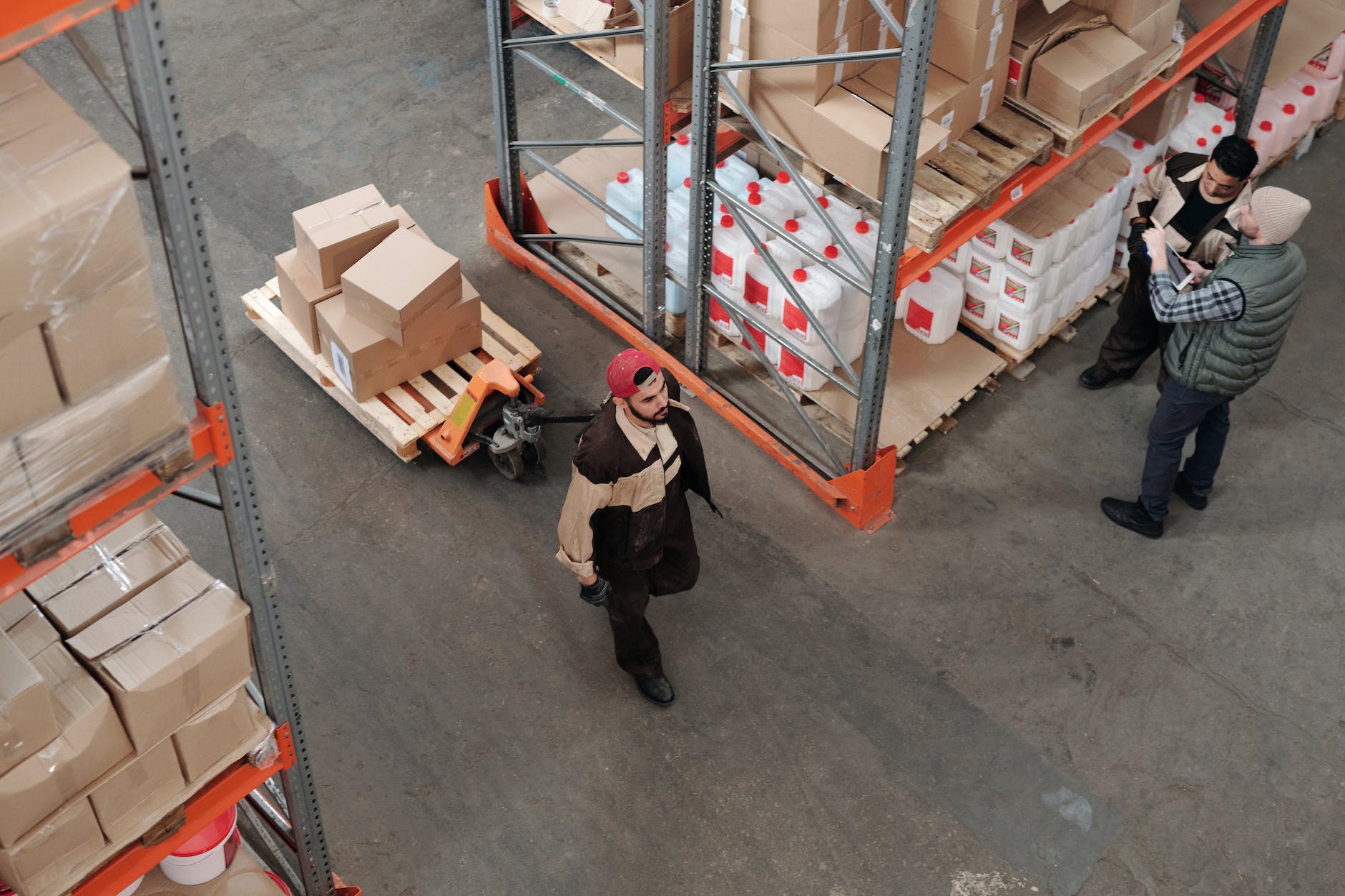
Modern Warehousing
Modern warehousing has undergone a paradigm shift, transforming from traditional manual processes to highly automated systems. The integration of robotics into warehouse operations has played a pivotal role in shaping this evolution. Let’s delve into the various facets of how robotics has become a linchpin in modern warehousing.
Definition of Modern Warehousing
In the 21st century, warehousing has transcended the conventional image of static storage spaces. Modern warehousing is a dynamic ecosystem encompassing advanced technologies that optimize storage, retrieval, and overall logistics.
Evolution of Warehousing Practices
The journey of warehousing has seen a remarkable evolution. From manual inventory management to sophisticated tracking systems, the industry has continuously adapted to meet the demands of an ever-changing market.
Introduction to Robotics in Warehousing
The integration of robotics marks a revolutionary phase in modern warehousing. Robots are no longer confined to manufacturing floors; they have found a vital place in the heart of logistics.
Benefits of Robotics in Warehousing
Increased Efficiency
Robotics has significantly boosted operational efficiency within warehouses. Automated processes, such as picking and packing, are executed with precision and speed, reducing the time required to fulfill orders.
Cost Reduction
While the initial investment in robotics may seem significant, the long-term benefits include a substantial cost reduction. Robots work tirelessly without breaks, minimizing labor costs and optimizing resource utilization.
Improved Accuracy
Human errors in inventory management can have severe repercussions. With robotics, the margin for error is drastically reduced, ensuring accurate tracking and fulfillment of orders.
Enhanced Safety
Dangerous and repetitive tasks can be delegated to robots, enhancing workplace safety for human employees. Collaborative robots work alongside humans, mitigating risks in the warehouse environment.
Types of Robotics Used in Warehousing
Horizontal and Vertical Carousel Storage Systems
Warehouse lift modules, including both VLM machine (Vertical Lift Module) and Horizontal Lift Module, revolutionize storage efficiency. These automated systems optimize vertical and horizontal space, utilizing trays or bins that can be accessed by robotic mechanisms. This innovation significantly enhances operational efficiency by reducing labor costs, minimizing errors, and maximizing storage density.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
AMRs navigate warehouses autonomously, transporting goods from one location to another. They adapt to changing environments, optimizing their routes for efficient operations.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
AGVs follow predetermined paths, streamlining material handling within warehouses. They are particularly useful for tasks like transporting goods from storage to the loading dock.
Robotic Arms
Equipped with advanced sensors, robotic arms excel at tasks requiring precision, such as picking items from shelves or assembling products.
Drones in Warehousing
Drones offer a bird’s-eye view of warehouse operations. They are employed for inventory tracking, surveillance, and even last-mile delivery in some cases.
Integration of Robotics with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
Streamlined Operations
Integrating robotics with WMS ensures seamless coordination between various warehouse functions. Real-time communication and data exchange contribute to streamlined operations.
Real-time Data and Analytics
Robotics generates vast amounts of data, providing insights into warehouse performance. Analyzing this data in real time enables informed decision-making for optimizing processes.
Inventory Management
Accurate and timely inventory management is critical in warehousing. Robotics, when integrated with WMS, facilitates precise tracking, reducing instances of stockouts or overstock.
Challenges and Solutions
Initial Implementation Challenges
The adoption of robotics in warehousing poses initial challenges, including the need for employee training and system integration. Companies must invest in comprehensive onboarding programs to facilitate a smooth transition.
Maintenance and Upkeep
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensuring the longevity of robotic systems. Establishing routine check-ups and employing predictive maintenance technologies mitigate the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
Workforce Adaptation
As robotics becomes integral to warehouse operations, employees need to adapt to working alongside machines. Continuous training programs foster harmonious collaboration between human and robotic workers.
Cybersecurity Concerns
With increased connectivity, warehouses become vulnerable to cyber threats. Robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption and regular security audits, are imperative to safeguard sensitive data.
Future Trends in Robotics for Warehousing
Artificial Intelligence Integration
The future of robotics in warehousing involves deeper integration with artificial intelligence. AI-driven robots will possess advanced decision-making capabilities, further enhancing operational efficiency.
Collaborative Robotics
Collaborative robots, or cobots, will become more prevalent, working alongside humans in intricate tasks. This collaborative approach maximizes efficiency and ensures the safety of human workers.
Sustainable Robotics
Environmental sustainability is a growing concern. Future robotics in warehousing will likely prioritize eco-friendly technologies, contributing to a greener supply chain.
Robotics’ Impact on Employment
Redefining Job Roles
While robots take over routine tasks, human employees can focus on more complex and strategic aspects of warehouse management. Upskilling programs ensure that the workforce remains relevant and valuable.
Job Creation vs. Job Displacement
Contrary to fears of job displacement, the integration of robotics in warehousing can lead to job creation. New roles emerge in the maintenance, programming, and oversight of robotic systems.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Compliance with Regulations
As the use of robotics in warehousing expands, adherence to regulatory standards becomes paramount. Companies must ensure that their robotic systems comply with safety and ethical guidelines.
Ethical Use of Robotics in Warehousing
Ethical considerations, such as ensuring fair treatment of human and robotic workers, must be at the forefront of warehouse management. Establishing ethical guidelines prevents the exploitation of technology.
The Future Landscape of Warehousing
Evolutionary Changes
The future promises continuous evolution in warehousing practices. Robotics will play a central role in shaping the landscape, contributing to more agile, responsive, and efficient warehouse ecosystems.
Global Adoption of Robotics
The adoption of robotics in warehousing is not limited to specific regions. Global players recognize the benefits and are increasingly incorporating robotics into their logistics strategies.
Conclusion
The role of robotics in modern warehousing cannot be overstated. From enhancing efficiency to reshaping job roles, robotics has become an indispensable asset in the warehouse of the future.
As we move forward, the integration of robotics will continue to redefine how we perceive and operate within warehouses. Embracing this technological evolution ensures competitiveness and sustainability in the ever-changing landscape of modern warehousing.