Future of Flexible Work Arrangements
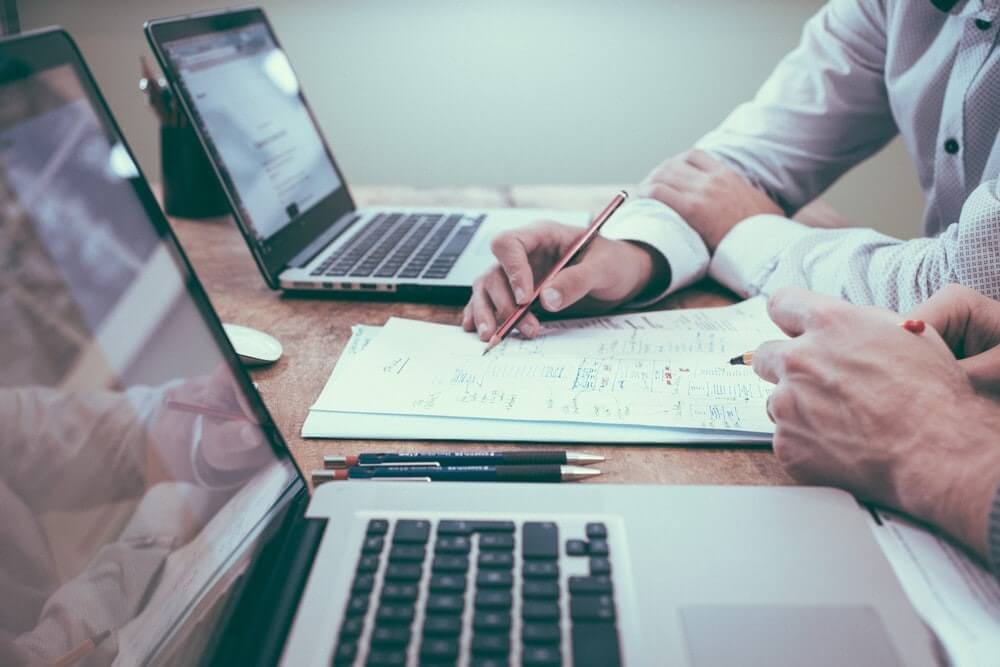
The gig economy has revolutionized the way we think about work, offering unprecedented flexibility and autonomy to a growing workforce of independent contractors, freelancers, and part-time workers. This shift towards more fluid work arrangements reflects broader changes in the global economy, driven by technological advancements, changing worker preferences, and evolving business needs. As we navigate the future of work, understanding the dynamics of the gig economy is crucial for both workers and employers. This article explores the key aspects of the gig economy, its benefits, challenges, and the strategies for success within this new paradigm.
The Rise of the Gig Economy:
“The gig economy has seen exponential growth over the past decade, fueled by the proliferation of digital platforms that connect freelancers with short-term work opportunities. This model offers workers the freedom to choose when, where, and how much they work, breaking away from the traditional 9-to-5 job structure. For employers, the gig economy provides access to a global talent pool and the flexibility to scale their workforce up or down based on demand, without the overhead associated with full-time employees.” Says Natalia Dávila Merlo, Content Marketing Manager at Ling.
The appeal of the gig economy is not just its flexibility but also the diversity of opportunities it presents. From ride-sharing and food delivery to professional consulting and creative services, the gig economy encompasses a wide range of industries and skill levels. This democratization of work has opened up new pathways for income generation and career development, particularly for those who may have been marginalized in the traditional job market.
Benefits of Flexible Work Arrangements:
One of the most touted benefits of the gig economy is the flexibility it offers to workers. This flexibility allows individuals to tailor their work schedules to fit their personal lives, rather than the other way around. For many, this means the ability to pursue passions, spend more time with family, or attend to personal health without the constraints of a rigid work schedule. The autonomy associated with gig work can lead to greater job satisfaction and a better work-life balance.
Sai Blackbyrn, CEO of Coach Foundation says “For businesses, the gig economy offers the advantage of agility. Companies can quickly adapt to market changes and business needs by tapping into a flexible workforce. This agility is particularly valuable in industries where demand can fluctuate unpredictably. Moreover, the gig economy allows companies to access specialized skills on an as-needed basis, enhancing their ability to innovate and compete in a rapidly changing business environment.”
Challenges and Uncertainties:
“Despite its benefits, the gig economy also presents significant challenges and uncertainties, particularly for workers. The lack of job security, benefits, and labor protections that are typically afforded to full-time employees can leave gig workers vulnerable. The fluctuating nature of gig work can lead to income instability, making it difficult for some workers to manage financial planning and access to credit.” Says Daniel Foley, head of content at Believe Money.
Moreover, the gig economy raises important questions about the future of work and social contracts. As more people move into gig work, there is a growing debate about how to ensure fair labor practices, adequate social protections, and access to benefits like health care and retirement savings. Addressing these challenges requires innovative policy solutions and a rethinking of traditional employment models.
Navigating Success in the Gig Economy:
“Success in the gig economy requires a proactive and strategic approach. For workers, this means continuously developing skills, leveraging digital platforms to find opportunities, and building a strong personal brand. Networking and community engagement are also crucial for finding new gigs and learning from peers. Additionally, gig workers must be adept at managing the administrative aspects of freelancing, such as financial planning, taxes, and health insurance.” Says Greg Webber, COO of Reliable Equipment.
Employers, on the other hand, need to develop effective strategies for managing a gig workforce. This includes clear communication of project expectations, fair compensation practices, and the creation of systems for feedback and performance evaluation. Companies that can successfully integrate gig workers into their workforce will benefit from increased flexibility, access to talent, and the ability to innovate more rapidly.
The Future of Work and Policy Implications:
“The gig economy is reshaping the future of work, prompting a reevaluation of employment policies and labor laws. As the gig economy continues to grow, there is a pressing need for policies that protect gig workers while supporting the flexibility and innovation that the gig economy offers. This might include new approaches to benefits, taxation, and worker classification that reflect the unique nature of gig work.” Says Jessica Shee from iBoysoft.
Furthermore, the gig economy highlights the need for lifelong learning and skill development as workers navigate changing job markets. Educational institutions and policymakers must adapt to provide workers with the skills and knowledge they need to thrive in a gig-based economy. This includes not only technical skills but also the entrepreneurial and self-management skills essential for success in gig work.
Conclusion:
The gig economy represents a significant shift in the nature of work, offering both opportunities and challenges for workers and employers alike. As we navigate this new landscape, flexibility, innovation, and adaptability will be key to success. For workers, this means embracing the autonomy and opportunities of gig work while advocating for fair labor practices and protections. For employers, it involves leveraging the benefits of a flexible workforce while ensuring fair and effective management practices.
As we look to the future, the gig economy prompts important questions about the nature of work, employment, and social protection in the 21st century. Addressing these questions will require collaborative efforts from businesses, policymakers, and workers themselves to ensure that the gig economy benefits all participants. With the right approaches, the gig economy has the potential to offer a more flexible, inclusive, and dynamic model of work for the future.