The Essential Components of a Successful PCB Assembly Process
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Assembly: The Art of Connecting Electronics
With the advent of technology, the production of electronic devices has reached new heights. Every device, be it a mobile phone, computer, or medical equipment, requires a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) to connect its components and ensure seamless functioning. The process of producing PCBs is referred to as PCB Assembly and is an art that requires an in-depth understanding of the components used, the techniques applied, and the quality control measures involved.
Printed circuit board assembly is a multi-step process that starts with designing and fabricating the PCB itself, followed by placing the components on the board and soldering them into place. The last but critical step is ensuring the quality of the assembly through visual inspection, testing, and environmental stress testing. In this article, we delve deeper into the various aspects of PCB Assembly, explaining each step in detail.
PCB Design and Fabrication: The Foundation of a PCB Assembly
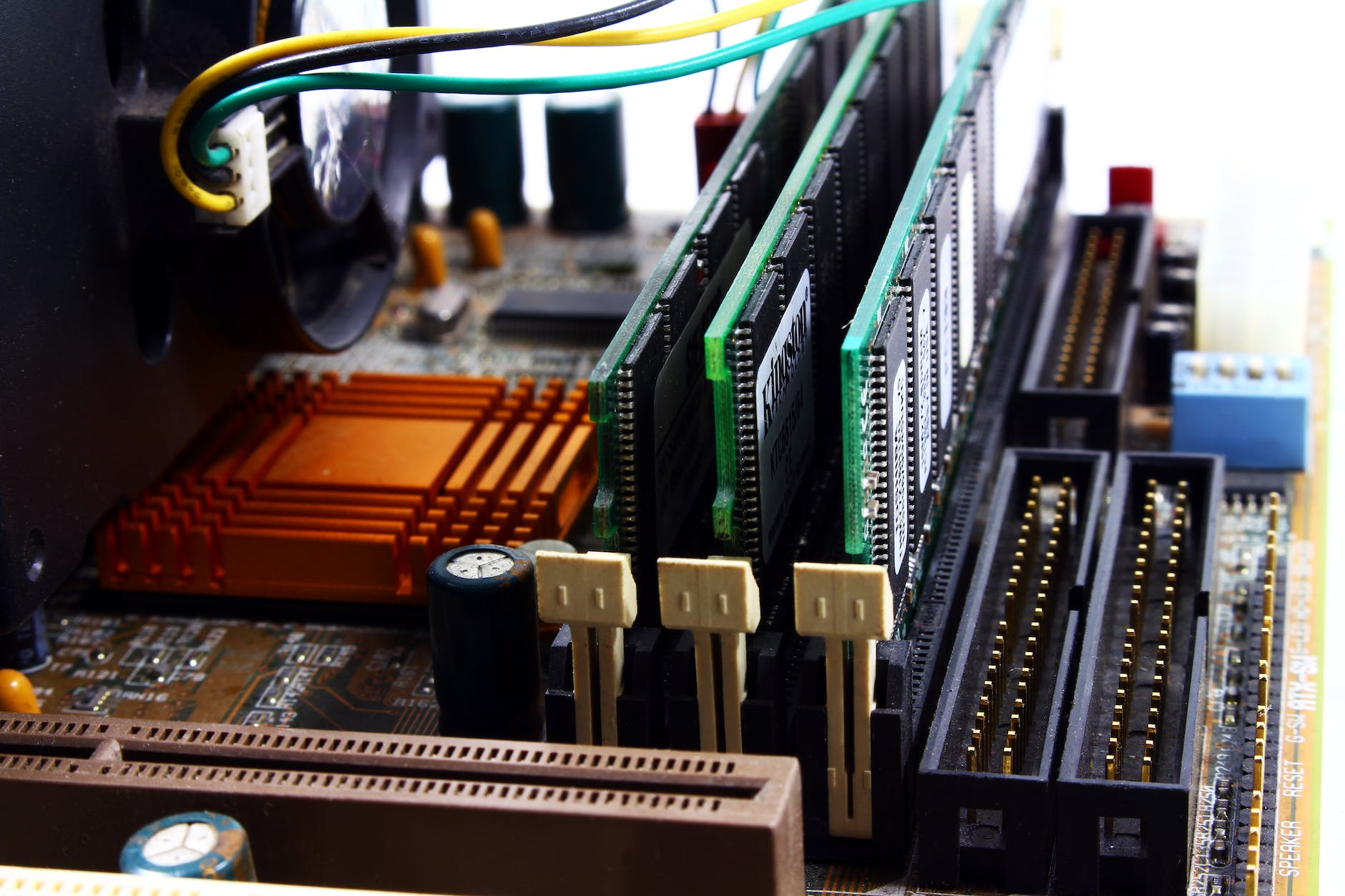
The first and foremost step in a PCB Assembly is designing and fabricating the printed circuit board. The board serves as the foundation for connecting the components and ensuring reliable performance. PCB fabrication starts with selecting a suitable substrate for the board and etching out traces for each component connection. Drilling holes for mounting components, and laminating layers to form multi-layer boards are part of the process.
Once the board has been fabricated, the next step is to start assembling components onto it. The choice of substrate and the number of layers determines the reliability and performance of the PCB, making it essential to choose carefully.
Component Placement and Soldering: The Heart of PCB Assembly
The next step in PCB Assembly is placing components onto the board and soldering them into place. The most common technique used is Surface Mount Technology (SMT), which involves placing components directly onto contact pads on the surface of the board. Automated pick-and-place machines or manual placement methods such as tweezers or vacuum pickup tools are used for this purpose.
Once the components are placed, they must be soldered into place. This process ensures that the components are securely attached to the board and ready to function. The choice of soldering technique and the quality of the soldering process determine the reliability of the assembly.
Quality Control Measures: The Final Frontier of PCB Assembly
PCB Assembly is a complex process that requires stringent quality control measures to produce reliable products. The quality of a PCBA is determined by the materials used, the design, production processes, and testing methods used during its assembly. Quality control measures can be divided into three categories: Visual Inspection, Testing Methods, and Environmental Stress Testing.
Visual Inspection involves checking the components and the board for defects such as shorts and opens caused by improper soldering, missing parts, or incorrect placement of components. This inspection can be done manually or with automated vision systems that detect even very small defects in the components or boards.
Testing Methods such as X-Ray Inspection, Automated Optical Inspection (AOI), Functional Testing, and In-Circuit Testing provide further insight into how well a PCBA performs under various conditions. X-ray inspection allows technicians to inspect the inside of the assembled board for hidden faults, while AOI uses high-resolution cameras to detect any irregularities on both sides of the board. Functional testing ensures that all components are functioning correctly, while In-Circuit Testing tests each component individually for voltage drops or current leakage.
Conclusion
PCB Assembly is a critical step in the production of many electronic devices. It requires a combination of advanced techniques and quality control measures to produce reliable and functional products.






